The main disadvantage of using static sites generators like Jekyll is that there is no easy, straightforward way to schedule posts that should be published at some point in the future. This is because your site is being built when you push a new commit to GitHub Pages.
A lot of people have struggled to make scheduling posts in Jekyll possible. You can find more on this topic (and some other references to other methods) in the article titled “How to Schedule Jekyll Posts on Github Pages” by Alex Learns Programming.
The methods from the above mentioned article use some paid solutions (Zapier, AWS) or force you to have or buy a server on which you may run cron jobs. If you host your site on your own server, the solution with cron jobs is definitely for you.
What I will show in this article is scheduling posts using GitHub Pages and Travis CI (both services are free to use).
1. Connect your GitHub repo with Travis CI
First of all, you have to connect your GitHub repository (where you store your site’s source files) with Travis CI. You can read about this integration in Travis CI documentation.
2. Enable cron jobs on Travis CI
To be able to schedule posts, someone or something has to make a commit to your GitHub repo, so it could be rebuilt. This will be the job of Travis CI that will run a cron job once a day.
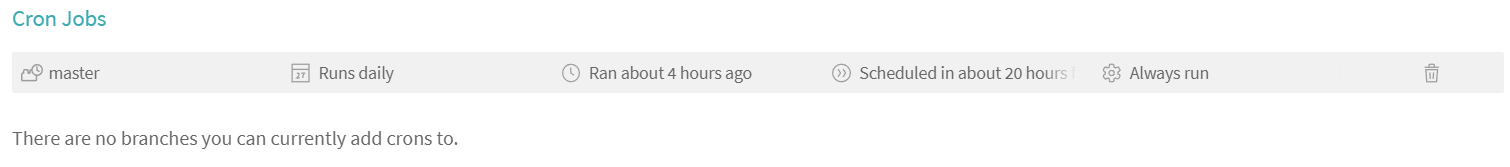
To enable cron jobs on Travis CI open More options -> Settings in the top-right corner of Travis CI administration panel. After that, scroll down to the bottom until you see Cron Jobs section. Add a daily cron job using your master or gh-pages branch. After that, you should get the similar result:
3. Generate Personal Access Token
This token is needed to allow Travis pushing commits to your repo. To create such a token follow the instruction on this page.
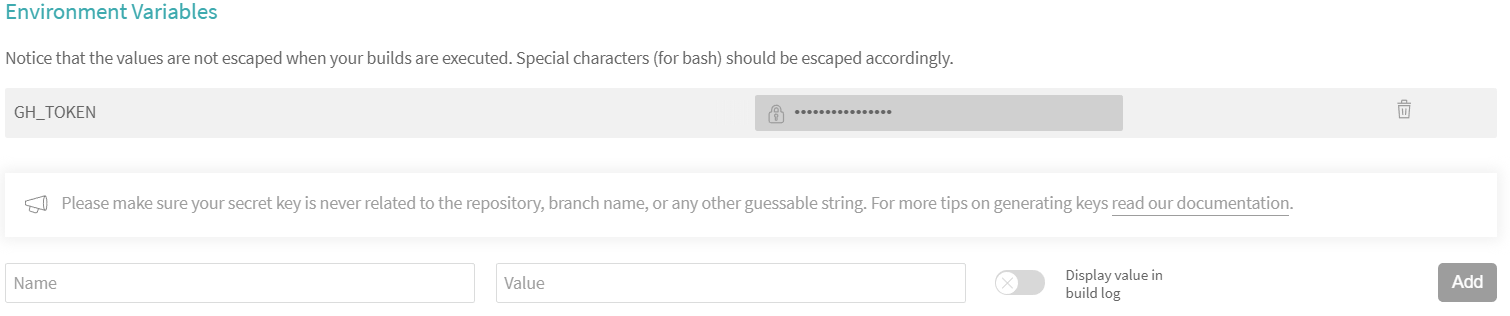
When you have your token, go back to Travis CI settings and in the Environment Variables section, paste the token in the value field and in the name field type GH_TOKEN which will be the variable name where your token will be stored. Also make sure not to display value in the build log.
After this operation you should have something like this in your settings:
4. Configure jekyll for future posting
Go to your site’s _config.yml file and set the future tag to false: future: false.
This will disable building posts with future dates.
5. Create Travis script
In your root site’s folder create a new file and name it .travis.yml. This is the script that will be launched by Travis when you commit something new to your GitHub repo or when the cron job will be triggered.
Then, paste the following code to this file:
language: ruby
rvm:
- 2.4.4
# Assume bundler is being used, therefore
# the `install` step will run `bundle install` by default.
script: chmod +x ./script/jekyll-rebuild.sh && ./script/jekyll-rebuild.sh
exclude: [vendor]
# branch whitelist, only for GitHub Pages
branches:
only:
- master # test the master branch
sudo: false # route your build to the container-based infrastructure for a faster build
cache: bundler # caching bundler gem packages will speed up build
# Optional: disable email notifications about the outcome of your builds
notifications:
email: false
What .travis.yml bascially does is it runs another bash script script/jekyll-rebuild.sh. In your root directory create a new folder script and inside this newly created directory create jekyll-rebuild.sh file. Inside this file paste the following code:
#!/bin/bash
# skip if build is triggered by pull request
if [ $TRAVIS_PULL_REQUEST == "true" ]; then
echo "this is PR, exiting"
exit 0
fi
# enable error reporting to the console
set -e
# cleanup "_site"
rm -rf _site
mkdir _site
# clone remote repo to "_site"
git clone https://${GH_TOKEN}@github.com/YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME/YOUR_GITHUB_REPO --branch master _site
# build with Jekyll into "_site"
# exec jekyll build
# push empty commit
cd _site
git config user.email "your@email.com"
git config user.name "Your_Username"
git commit -a -m "rebuild pages" --allow-empty
git push origin master
# remove last empty commit
git reset HEAD~
git push origin master --force
This is the script where all the “magic” happens. This script clones your repo, creates an empty commit, pushes it to your GitHub repo (which will force rebuilding of your jekyll site). After that, it removes this empty commit as if it was never there.
And that’s it. Scheduling posts with jekyll using GitHub Pages and Travis CI should be configured now.
Does it work?
If you see this post and my other posts on this site it surely works ![]()
Final remarks
I hope this solution was helpful to you. If you still can’t get it working, look at my scripts on my GitHub repo or write a comment in the section down below.